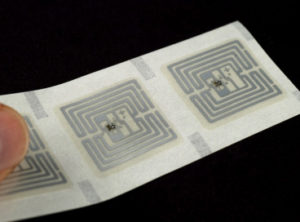
RFID tags
An RFID tag, also known as an electronic tag, a smart tag, or a transponder, is an electronic identification technology which does not need to be seen to be read. It is possible to read and write information, beyond a simple serial number, stored in the memory on the chip. These two characteristics set them apart from bar codes.
-
 Wet or Dry tags
Wet or Dry tags -
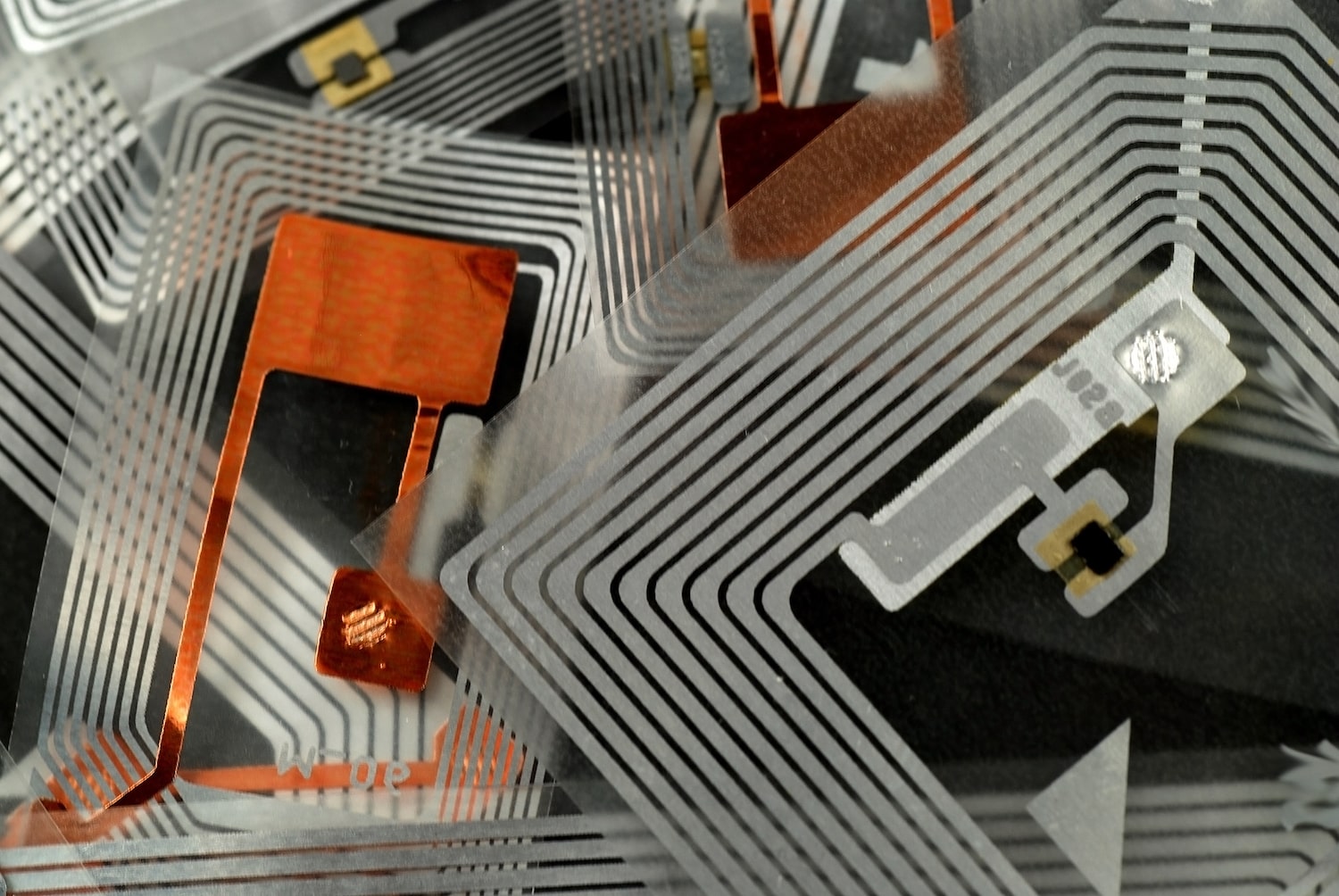
 RFID Wet Inlays refer to RFID tags with an adhesive backing, designed for convenient attachment to various surfaces. Each RFID Inlay comprises an IC/Chip along with a dipole antenna. These Wet Inlays can be likened to RFID stickers and are particularly well-suited for applications that demand a hassle-free "peel and stick" tag solution. RFID Dry Inlays are devoid of adhesive backing, unlike RFID Wet Inlays. Instead, they secure an IC and an antenna to a substrate or material. These Dry Inlays have a resemblance to laminated RFID Tags.
RFID Wet Inlays refer to RFID tags with an adhesive backing, designed for convenient attachment to various surfaces. Each RFID Inlay comprises an IC/Chip along with a dipole antenna. These Wet Inlays can be likened to RFID stickers and are particularly well-suited for applications that demand a hassle-free "peel and stick" tag solution. RFID Dry Inlays are devoid of adhesive backing, unlike RFID Wet Inlays. Instead, they secure an IC and an antenna to a substrate or material. These Dry Inlays have a resemblance to laminated RFID Tags. -
 Printed labels with tags
Printed labels with tags - RFID, an abbreviation for Radio Frequency Identification, involves the use of radio waves for transmitting information to other devices. When an RFID label comes into proximity with a dedicated reader device, the radio waves emitted by the reader activate the chip within the label, enabling it to transmit information back to the reader.
-
 Pre-encoded tags
Pre-encoded tags -
Pre-encoded RFID tags refer to radio frequency identification (RFID) tags that have already been programmed with data before they are distributed or sold. The data stored in these tags can include unique identifiers, product information, or other relevant details depending on the intended application.
When a tag is pre-encoded, the information is typically written to the integrated circuit (IC) or chip within the tag during the manufacturing process. This data cannot be altered or modified after the encoding, making it a read-only RFID tag. These pre-encoded tags are ready to use upon purchase, and their data remains fixed throughout their lifespan.
Pre-encoded RFID tags find applications in various industries, such as inventory management, supply chain tracking, access control, and asset tracking, where having consistent and unchangeable data on the tag is essential for reliable and secure operations.
-
 UHF or NFC
UHF or NFC -
UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) and NFC (Near Field Communication) are two different types of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technologies, each with its own characteristics and use cases. Here are the key differences between UHF RFID tags and NFC RFID tags:
1- Frequency Range:
UHF RFID Tags: UHF RFID operates in the frequency range of 860 to 960 MHz. This frequency range allows for longer read ranges, typically several meters, making UHF tags suitable for applications that require reading tags from a distance, such as inventory management in warehouses or tracking assets in large areas.
NFC RFID Tags: NFC operates at a much lower frequency of 13.56 MHz. The read range of NFC tags is very short, usually a few centimeters at most. This close-proximity communication makes NFC ideal for applications that require secure and quick interactions between devices, like contactless payments or data exchange between smartphones.2- Read Speed:
UHF RFID Tags: UHF RFID tags can be read relatively quickly, even when dealing with a large number of tags simultaneously. This makes them efficient for bulk scanning operations and high-speed applications like toll collection on highways or race timing systems.
NFC RFID Tags: NFC tags offer a fast read speed, especially considering the close proximity required for communication. They are well-suited for rapid data exchange, such as tapping an NFC-enabled card on a payment terminal for a quick transaction.
3- Data Capacity:
UHF RFID Tags: UHF tags typically have a larger memory capacity, allowing them to store more data, such as detailed product information or unique identifiers for large-scale supply chain applications.
NFC RFID Tags: NFC tags usually have a smaller memory capacity compared to UHF tags. They are often used to store smaller amounts of data, such as web links, contact information, or authentication tokens.4- Applications:
UHF RFID Tags: UHF RFID tags are commonly used in applications like logistics, retail inventory management, asset tracking, and supply chain management, where long-range reading capabilities and the ability to handle a large number of tags simultaneously are essential.
NFC RFID Tags: NFC tags are prevalent in contactless payment systems, public transportation fare systems, access control for buildings or events, smart posters, and other applications that require secure, short-range communication between devices.In summary, UHF RFID tags are best suited for applications that require long-range reading and handling a large number of tags, while NFC RFID tags are ideal for secure, close-proximity interactions between devices. The choice between UHF and NFC depends on the specific requirements of the application and the desired read range and data capacity.
An RFID system is composed of an RFID tag, a reader or encoder which can be used to read or write data to the chip on the tag, and a computer system able to collect and process this data.
An electronic tag consists of an electronic chip connected to an antenna. This can function at low or high frequencies, and may be passive or active. Passive tags have read-only functionality, while active tags make it possible to read from and write data to the chip.
An RFID tag may have several forms, depending on the criteria defined for the desired tracking project.
We offer a wide selection of tags and LF, HF and UHF inlays, depending on your tracking needs and constraints.
These tags and inlays may be complexed, printed and decorated with various support materials (foams, polycarbonates, polyesters, etc.), to ensure total protection and personalisation of your RFID tags.
Don’t hesitate to contact us with any request. Gravic will assist and advise you on your complete RFID project, relying on all our partners.
ELECTRONIC RFID TAG
An RFID tag, also known as an electronic tag, smart tag, or transponder, is an electronic identifier that does not need to be viewed in order to be read. It is therefore possible to read and write information other than a simple serial number in the chip’s memory. These two features distinguish it from a barcode. You can trust Gravic Group, an expert in printed and stamped material, to help you deliver your RFID tag project
How does an RFID tag work?
An RFID system consists of an RFID tag, a drive or encoder that can be used to read or write data on the tag’s chip, and an IT system allowing these data to be collected and processed.Not to be confused with an engravable tag, an electronic tag consists of an electronic chip connected to an antenna. It can operate at high or low frequencies and be passive or active. A passive tag is ready-only, whilst an active tag allows data on the chip to be read and written.
What are the different types of rfid tag?
An RFID tag can come in different forms based on the criteria defined by the level of traceability you wish to aim for in your project.We offer a wide range of RFID tags and LF, HF and UHF inlays to meet your traceability needs and obligations. These tags and inlays can be bound, printed and decorated with different materials (foam, polycarbonates, polyesters etc.) to ensure full protection and personalisation for your RFID tags.Feel free to contact us if you have any enquiries. All our partners at Gravic will be happy to give you help and advice for your global RFID project. Also discover all our adhesive tag making services.

123, Zone Industrielle de l’Argile II, 06370
Mouans Sartoux, FRANCE
Tel. +33 (0)4 93 75 75 34



深圳市格瑞维克电子科技有限公司
深圳市南山区南山街道向南社区海德二道470号海德大厦A1002A
Shenzhen, CHINA